Rice is the most significant food crop on the globe. The annual rice production is anticipated to be over 700 million tonnes. Rice bran is a valuable byproduct of rice milling. In India, around 63 million tonnes of rice bran are produced. Rice bran oil is made from rice bran, which is collected from unpolished rice through the milling process.
Rice bran oil is a pale-yellow translucent oil with a subtle nutty flavour that is light and odourless. The primary components of crude rice bran oil are free fatty acids, phospholipids, waxes, and glycerides. Because of its high smoke point, the oil is suitable for high-temperature cooking methods such as deep frying and stir frying.
Rice bran oil is popularly referred to as "Wonder Oil" due to its numerous health advantages. Rice bran oil is popular in the Middle East, South America, and Africa. The global market for rice bran oil is expected to grow at a 3.0 percent CAGR from 2021 to 2026, from 124.2 million USD in 2020 to 153.1 million USD at the end of 2026. Rice bran oil brands available in India include "Fortune," "Saffola," "Dhara Life," and others. Other than cooking, rice bran oil is used in cosmetics, medicines, food processing, and other sectors.
Nutritional composition
Rice bran oil has a strong nutritional profile (Table 1) due to its optimal fatty acid content and bioactive phytonutrients (Table 2). It contains tocopherol and γ-oryzanol. Rice bran oil has a number of health benefits, including the prevention and treatment of colon cancer, AIDS, obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels, as well as increasing energy, reducing allergies, strengthening immunity, and decreasing irritable menopause symptoms.
Table 1: Rice-bran oil physicochemical and nutritional components (Sneh Punia et.al, 2021)
|
Physicochemical parameters |
Value |
|
Acid value |
< 0.1 |
|
Saponification value |
180-195 |
|
Iodine value |
|
|
Refractive index |
1.46- 1.47 |
|
Moisture |
<0.1 |
|
Unsaponifiable matter |
3-5% |
|
Wax |
3-4% |
|
Steryl esters |
2.8–3.1% |
|
Monoacylglycerol |
1-2% |
|
Diacylglycerols |
2-3% |
|
Triacylglycerols |
81-84% |
|
γ- Oryzanol |
0.9-2.9% |
|
Free fatty acids |
2-6% |
|
Tocopherols |
0.10–0.14% |
|
Saturated fatty acids |
23.63–24.7 |
|
Monounsaturated fatty acids |
43-445 |
|
Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
31–33.6% |
Table 2: Bioactive phytonutrients in Rice bran oil (Ali and Devrajan 2017)
|
Bioactive components |
Functions |
|
Oryzanol |
Essential phytochemical, Cholesterol reducing property, prevent cancer, antioxidant activity |
|
Tocotrienols |
Skin softening, skin repairing, anti-cancer effect |
|
Phytosterols |
Enhance immune system |
|
Squalene |
Skin repairing and skin whitening |
|
Tocopherols |
Blood vessel health and immune function, improve neurological functions, balance endocrine hormones |
Rice bran oil is distinguished from other oils by its high smoke point, aroma, absence of greasiness, palatability, ease of cleanup, and appropriate fat content, among other characteristics. Rice bran oil is one of the healthiest edible oils due to its balanced composition of monounsaturated, saturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids. It has a fatty acid composition that is similar to WHO standards, 1:1.5:1 ratio of saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, and polyunsaturated fatty acids (WHO, 2008).
Rice bran oil has two major issues: The first is a lack of omega-3 fatty acids; nevertheless, rice bran oil has more omega-6 fatty acids, which raises the risk of breast and prostate cancer. Another major issue is the high arsenic level, which causes stomach pain, irregular bowel motions, and intestinal gas. As a result, up to 30 grammes of rice bran oil is recommended.
Conclusion
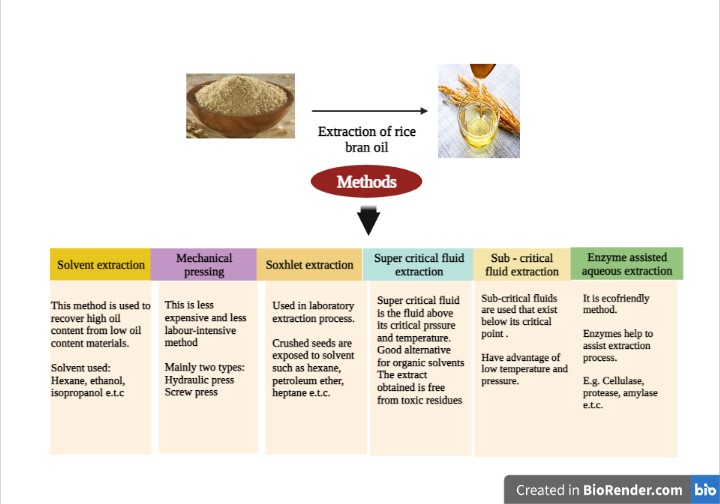
There are various methods for extracting RBO from bran (Figure 1). The bran obtained from rice grain is 8-10%, while the oil yield from rice bran is 18-22%. However, rather than extracting rice bran oil, a greater amount of rice bran is used as animal feed, chicken feed, and a huge proportion is discarded.
According to FAO 2018, India has the capacity to produce 1620 Kilometric Tons (KMT) of RBO, but actual production is just 960 KMT. This is because rice bran is underutilised. Humans, on the other hand, consume much less rice bran oil. RBO is gaining popularity due to its nutritional components, and it needs to be popularised among consumers as a healthy cooking oil substitute.
References:
- Ali, A., & Devarajan, S. (2017). Nutritional and health benefits of rice bran oil. In Brown Rice (pp. 135-158). Springer, Cham.Nutrition and applications of rice bran oil: a mini-overview, 2021
- Punia, S., Kumar, M., Sandhu, K. S., & Whiteside, W. S. (2021). Rice?bran oil: An emerging source of functional oil. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 45(4), e15318.
- WHO (2008). Interim summary of conclusions & dietary recommendations on total fat & fatty acids. The joint FAO/WHO expert consultation on fats & fatty acids in human nutrition. Geneva: WHO (pp. 1–14).
- Garba, U., Singanusong, R., Jiamyangyuen, S., & Thongsook, T. (2017). Extraction and utilization of rice bran oil: A review. safety, 17, 24.
- https://www.informmagazinedigital.org/informmagazine/october_2019/MobilePagedArticle.action?articleId=1523877#articleId1523877. https://indianexpress.com