World Zoonoses Day is celebrated on July 6th every year to raise awareness about zoonotic diseases and their impact on human and animal health. The term "zoonoses" refers to infections/diseases that are naturally transmitted from vertebrate animals to humans and vice versa. Out of 1415human pathogens identified, 868 (61%) are zoonotic in nature.
The zoonotic diseases are caused by various infectious agents of bacterial, viral, parasitic and fungal origin and can have serious health consequences in humans and animals.The few examples are brucellosis, anthrax, tuberculosis, rabies, Japanese encephalitis, Influenza etc. There has been emergence of zoonotic diseases across the world. A joint effort of United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) has identified seven reasons for the emergence of zoonotic diseasesviz., increased demand for animal protein; unsustainable agricultural intensification;increased use and exploitation of wildlife; unsustainable utilization of natural resources accelerated by urbanization, land use change and extractive industries; increased travel and transportation; changes in food supply; and climate change.
Socio-economic impact of zoonotic diseases:
The zoonotic diseases exhibit significant impact on humanity. For example, Rabies is known to kill around 25000 humans annually in the India; the number is highest in the world. Neurocysticercosis parasitic disease is responsible for nervous symptoms in infected humans; the famous Indian tennis player Leander Paes once suffered with neurocysticercosis. Brucellosis, a bacterial disease, is famously known to cause biphasic fever with joint pain in veterinarians, farmers and slaughter house workers. Toxoplasma gondii, transmitted from cats, causes abortion on pregnant ladies. These examples are just the tip of iceberg. Zoonotic diseases have been a significant threat to public health. Other important examples are SARS, swine flu, bird flu, MERS, Ebola, Nipah, and COVID-19.Therefore, it becomes imperative to create awareness on zoonotic diseases, their transmission from animals and educate people to adopt hygienic measures to prevent the infection of zoonotic diseases.
History of World Zoonoses Day:
World Zoonoses Day commemorates the work of French biologist Louis Pasteur. On 6 July 1885, Pasteur successfully administered the first human vaccine against rabiestoJoseph Meister, who was mauled by a rabid dog.Joseph Meister survived from the dog bite. World Zoonoses Day was first observed on July 6, 2007, the 100thanniversary of Louis Pasteur's death, to honor his contribution to the field of zoonotic diseases.
Significance of World Zoonoses Day:
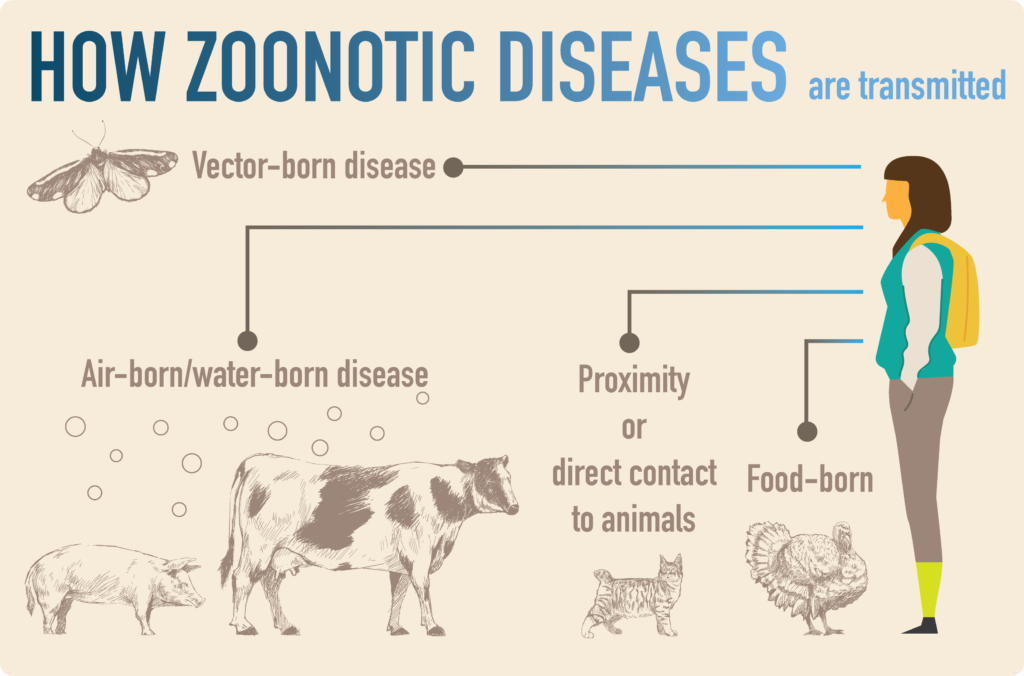
- World Zoonoses Day is a significant observance that highlights the importance of preventing and controlling zoonotic diseases. These diseases can be transmitted through direct contact with infected animals, consumption of contaminated food or water, or through bites of infected insects or ticks.
- The impact of zoonotic diseases on human health can be severe, causing a range of symptoms ranging from mild flu-like illnesses to severe respiratory infections, hemorrhagic fevers, and even death. These diseases can also have significant economic consequences, particularly in the livestock sector.
- World Zoonoses Day raises awareness about the risks and impacts of zoonotic diseases, and emphasizes the need for collaboration between different health science professionals, including veterinarians, medicos, andenvironmentalists under One Health approach.
- Through activities such as educational campaigns, conferences and workshops, public lectures, online events (webinars, live streams, and social media campaigns), community outreach, health screenings, animal welfare initiatives etc., World Zoonoses Day encourages individuals and organizations to take action to prevent and control zoonotic diseases. This includes measures such as improved surveillance, vaccination programs, better hygiene and sanitation practices, and increased collaboration between different health science professionals.
Recommendations to mitigate zoonotic diseases:
UNEP and ILRI has provided certain key recommendations to prevent future outbreaks of zoonotic diseases. These recommendations are:
- Raise awareness and increase understanding of zoonotic and emerging diseases
- Increased investments in interdisciplinary approaches including the One Health concept
- Expand scientific inquiry into the complex social, economic and ecological dimensions of emerging diseases, including zoonoses
- Cost-benefit analyses of the prevention of zoonotic diseases.
- Strengthening monitoring and regulating practices associated with zoonotic diseases, including food safety
- Incentives for sustainable food security and livelihoods, including wildlife source foods
- Improving biosecurity measures in animal husbandry or livestock production
- Integrated management of landscapes and seascapes that enhance sustainable co-existence of agriculture and wildlife
- Strengthen existing capacities among health stakeholders in all countries
- Operationalizing the One Health approach in land-use and sustainable development planning, implementation and monitoring, among other fields