Researchers have used liquid metals to turn carbon dioxide back into solid coal, in a world-first breakthrough that could transform our approach to carbon capture and storage.
The research team led by RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, have developed a new technique that can efficiently convert CO2from a gas into solid particles of carbon.
Published in the journal Nature Communications, the research offers an alternative pathway for safely and permanently removing the greenhouse gas from our atmosphere.
Current technologies for carbon capture and storage focus on compressing CO2 into a liquid form, transporting it to a suitable site and injecting it underground. But implementation has been hampered by engineering challenges, issues around economic viability and environmental concerns about possible leaks from the storage sites.
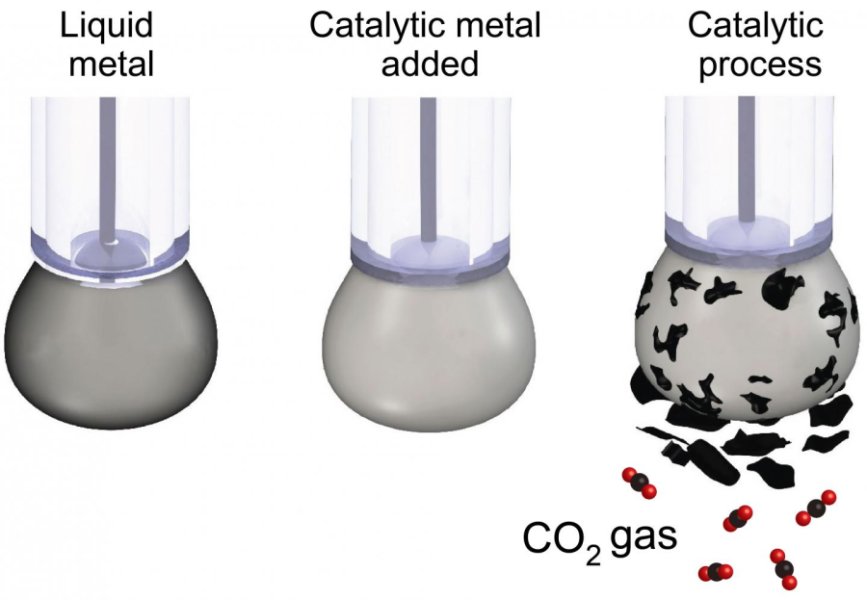
To date, CO2 has only been converted into a solid at extremely high temperatures, making it industrially unviable. By using liquid metals as a catalyst, researcher shown it's possible to turn the gas back into carbon at room temperature, in a process that's efficient and scalable.
To convert CO2, the researchers designed a liquid metal catalyst with specific surface properties that made it extremely efficient at conducting electricity while chemically activating the surface.
The carbon dioxide is dissolved in a beaker filled with an electrolyte liquid and a small amount of the liquid metal, which is then charged with an electrical current. The CO2 slowly converts into solid flakes of carbon, which are naturally detached from the liquid metal surface, allowing the continuous production of carbonaceous.