COVID-19
On January 7, 2020 Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, director-general of the World Health Organization (WHO), officials announced they had identified a new virus and named it 2019-nCoV.
COVID Vaccine
On Nov. 9, New York-based Pfizer and the German company BioNTech made history by presenting preliminary data indicating that their coronavirus vaccine was over 90 percent effective.
On Nov. 30, the Boston-based company Moderna announced it was applying to the Food and Drug Administration for an emergency use authorization, less than a year after it launched the first clinical trial for a coronavirus vaccine. Moderna reported 94.5% efficacy. The Gamaleya Research Institute, part of Russia’s Ministry of Health, has created a vaccine with an efficacy rate of 91.4 percent, according to a Dec. 14 announcement.
On Dec. 8, researchers with the University of Oxford and the British-Swedish company AstraZeneca published the first scientific paper on a Phase 3 clinical trial of a coronavirus vaccine. The trial demonstrated that the vaccine can protect people from Covid-19, but it left many questions unresolved about the results.
New cancer vaccine ready for human trials
A team of researchers has designed a novel cancer therapeutic vaccine that has the potential to treat numerous blood cancers as well as solid malignancies including breast, lung, renal, ovarian and pancreatic cancers. It works by targeting cancers that express a highly immunogenic tumor?associated antigen transcription factor Wilms' tumor 1 (WT1). The team published findings from a preclinical study in July 2020.
First animal-to-human transmission of deadly hantavirus identified in Germany
Germany’s first ever case of animal-to-human transmission of a form of hantavirus called the “Seoul virus” has been confirmed. Whilst hantaviruses spread by mice have been seen in Germany for a number of years, the Seoul virus is mainly found in Asia, transmitted exclusively by rats and known to cause severe disease in people. In this particular case, the virus was isolated from a seriously ill, young female patient and her pet rat. Viral sequencing determined both isolates were the same, confirming zoonotic transmission. This raised concerns regarding the potential import of disease in domesticated animals.
CRISPR’s big clinical tests
The CRISPR gene-editing tool faces key tests this year of its promise to treat cancer and genetic diseases. A small U.S. clinical trial is using CRISPR to disable three genes in T cells that are then returned to a cancer patient's body, an approach that could help these immune system soldiers stop malignant cells from growing and extend patients' lives. More results may also come from separate CRISPR cancer trials in China.
Oldest material found on Earth is more ancient than our solar system
Billions of years before our sun winked into existence, a dying star flung dust out into space. Now a bit of that stardust, trapped in a meteorite that collided with Earth, was dated as the oldest material yet found on our planet. The dust coalesced with other rocks inside what would become the Murchison meteorite, which lit up skies over Australia in September 1969 as it careened to the surface of our planet.
First tyrannosaur embryos discovered
Researchers have identified the remains of tyrannosaurs so young they hadn’t yet broken free from their shells. The discovery comes from finds at two different sites—a foot claw unearthed in 2018 from the Horseshoe Canyon Formation in Alberta, Canada, and a lower jaw recovered in 1983 from the Two Medicine Formation of Montana.
Timekeeping theory combines quantum clocks and Einstein's relativity
A phenomenon of quantum mechanics known as superposition can impact timekeeping in high-precision clocks, according to a theoretical study from Dartmouth College, Saint Anselm College and Santa Clara University. Research describing the effect shows that superposition the ability of an atom to exist in more than one state at the same time leads to a correction in atomic clocks known as "quantum time dilation."
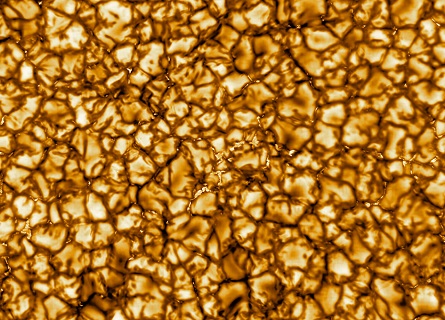
Highest-resolution image of the Sun ever taken
Astronomers have just released the highest-resolution image of the sun. Taken by the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope in Maui, it gives us an unprecedented view of our nearest star and brings us closer to solving several long-standing mysteries. The new image demonstrates the telescope’s potential power. It shows off a surface that’s divided up into discrete, Texas-size cells, like cracked sections in the desert soil. You can see plasma oozing off the surface, rising high into the solar atmosphere before sinking back into darker lanes.
Herpes virus code cracked
It had been assumed that there were approximately 80 open reading frames (ORFs) - locations in the genome where the information in DNA is read and translated into proteins - in the genome of herpes simplex virus 1. Using a broad range of the latest systems biology methods, scientists from the University of Würzburg and others revealed that there are actually a lot more. The teams identified 284 ORFs translated from hundreds of novel viral transcripts, which have now also been identified.