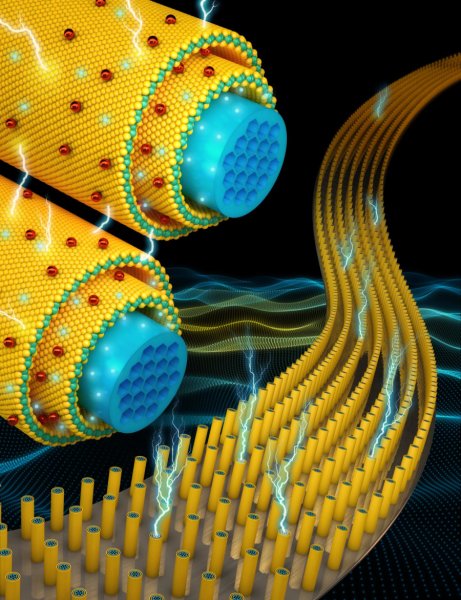
A team of UCF scientists has developed a new process for creating flexible supercapacitors that can store more energy and be recharged more than 30,000 times without degrading.
The novel method from the University of Central Florida's NanoScience Technology Center could eventually revolutionize technology as varied as mobile phones and electric vehicles.
"If they were to replace the batteries with these supercapacitors, you could charge your mobile phone in a few seconds and you wouldn't need to charge it again for over a week," said Nitin Choudhary, a postdoctoral associate who conducted much of the research published recently in the academic journal ACS Nano.
Anyone with a smartphone knows the problem: After 18 months or so, it holds a charge for less and less time as the battery begins to degrade.
Scientists have been studying the use of nanomaterials to improve supercapacitors that could enhance or even replace batteries in electronic devices. It's a stubborn problem, because a supercapacitor that held as much energy as a lithium-ion battery would have to be much, much larger.
The team at UCF has experimented with applying newly discovered two-dimensional materials only a few atoms thick to supercapacitors. Other researchers have also tried formulations with graphene and other two-dimensional materials, but with limited success.